What is a digital signature?
A digital signature is a mathematical technique used to validate the authenticity and integrity of a message, software or digital document. As the digital equivalent of a handwritten signature or stamped seal, a digital signature offers far more inherent security, and it is intended to solve the problem of tampering and impersonation in digital communications.
How digital signatures work
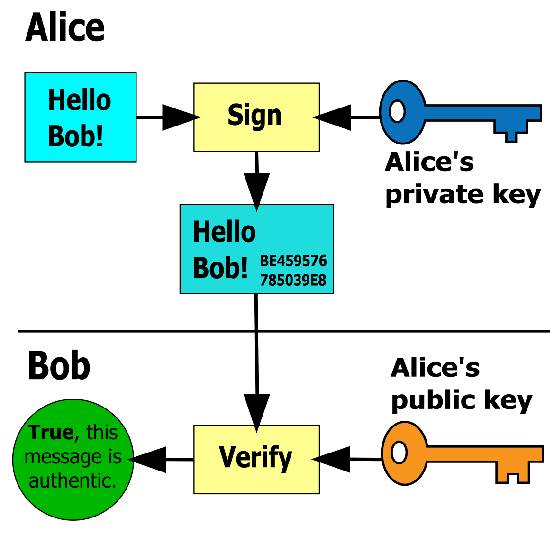
Digital signatures are based on public key cryptography, also known as asymmetric cryptography. Using a public key algorithm, such as RSA, one can generate two keys that are mathematically linked: one private and one public.
Digital signatures work through public key cryptography's two mutually-authenticating cryptographic keys. The individual who is creating the digital signature uses their own private key to encrypt signature-related data; the only way to decrypt that data is with the signer's public key. This is how digital signatures are authenticated.
Digital signature technology requires all the parties to trust that the individual creating the signature has been able to keep their own private key secret. If someone else has access to the signer's private key, that party could create fraudulent digital signatures in the name of the private key holder.